Chinese Dynasty Replacement Romance (P1)
China has a long history, and the change of dynasties is the best in the world. The history of faith in China began in Shang (oracle bone inscriptions, ruins of Yin Ruins), or in the first year of Zhou Gonghe (841 BC) recorded in Shi Qian's "Historical Records". There is no direct historical and archaeological data to prove the period.

1. Xia Dynasty (2070 BC - 1600 BC, 470years)
In 2205 BC, the chiefs of the tribes elected Yuwenming as the head of state of China, built the Xia Dynasty, and honored him as "Emperor Xia Yu, the capital of Anyi (Xia County, Shanxi). In 2198 BC, Jiwenming was death in Kuaiji (Yichuan, Henan), the tribal chiefs elected Ren Yi as emperor, and Jiwenming's son Jiqi was dissatisfied. Then Jiqi killed Ren Yi and succeed him as emperor. The end of China's election system, the beginning of family inheritance. Emperor Yu conquered Jiuzhou and used gold to cast nine tripods to show his achievements and prestige. Slavery society was roughly formed during the reign of Yu. The Xia Dynasty experienced a total of thirteenth and sixteenth kings.
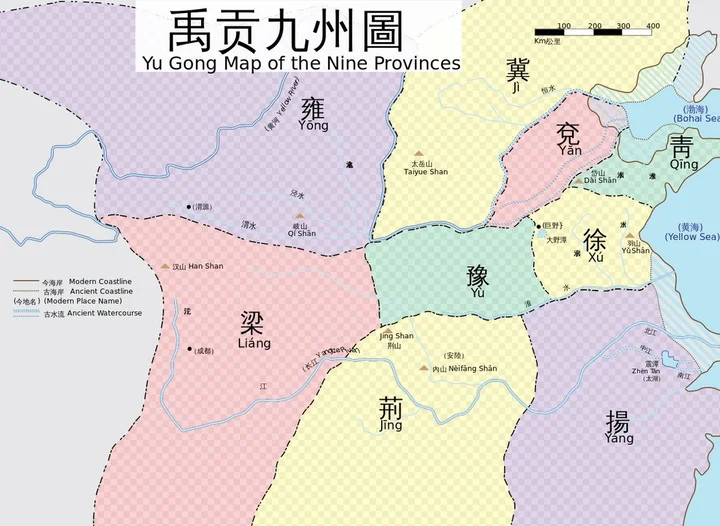
2. Shang Dynasty (1600 BC- 1046 BC, 554 years)
In 1766 BC, Zi Tianyi raised an army to go to the Gui Gui, and the Xia Dynasty fell. Zi Tianyi succeeded as emperor, established the Shang Dynasty, honored as "Tang Emperor of Shang", and established the capital Boyi (Cao County, Shandong). It was the first dynasty in China to have direct written records of the same period. The Shang Dynasty passed down a total of 31 kings in 17 generations. The system of succession to the throne of the Shang Dynasty, in the early stage, was the succession of brothers, and in the later stage, it was a typical succession of fathers and sons.
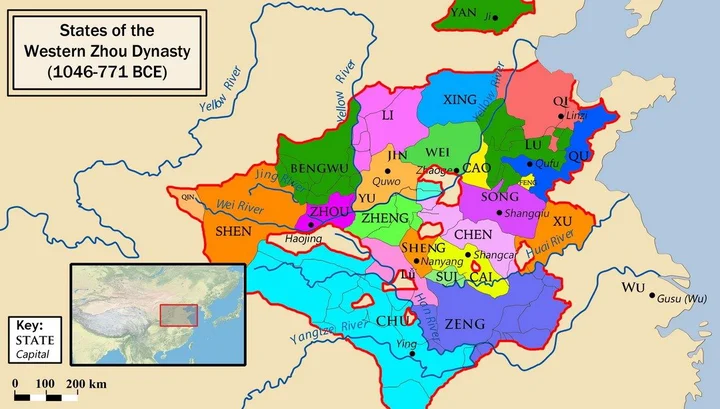
3-1. Zhou Dynasty (1046 BC- 256 BC, 791 years)
Western Zhou Dynasty (1046 BC- 771 BC, 276 years)
In 1122 BC, Ji Fa launched an army to resist the violence, and Zixin of the Shang Dynasty was defeated, self-immolated to death, and Yin died. Ji Fa succeeded as the head of state of China, renamed the king, built the Zhou Dynasty, and honored the title of King Wu. Ji Fa seals the princes. The capital was in Haojing (Zongzhou) (now southwest of Xi'an, Shaanxi); in the fifth year of Zhou Chengwang, the capital Luoyi (Chengzhou) was built (now Luoyang, Henan). In 771 BC, Quan Rong invaded the capital of the Western Zhou Dynasty, Haojing, and killed Ji Gonglu, and the Western Zhou Dynasty perished.
3-2. Zhou Dynasty (1046 BC- 256 BC, 791 years)
Eastern Zhou Dynasty (770 BC- 256 BC, 515 years)
After the demise of the Western Zhou Dynasty, the princes jointly supported Ji Yijiu, the son of Ji Gongnan, to succeed him. He was the King of Zhou Ping and moved the capital to Luoyang, known as the Eastern Zhou Dynasty in history. The language of the Zhou Dynasty was ancient Chinese, and ancient Chinese characters were still used in the writing. In the folk records, the tortoise bone and cow bone inscriptions were still the main records, and the royal family mainly used the emerging Jinbo and other records. The Zhou Dynasty implemented the system of feudal feudalism (the feudal state was established), and the King of Zhou was "the co-lord of the world".
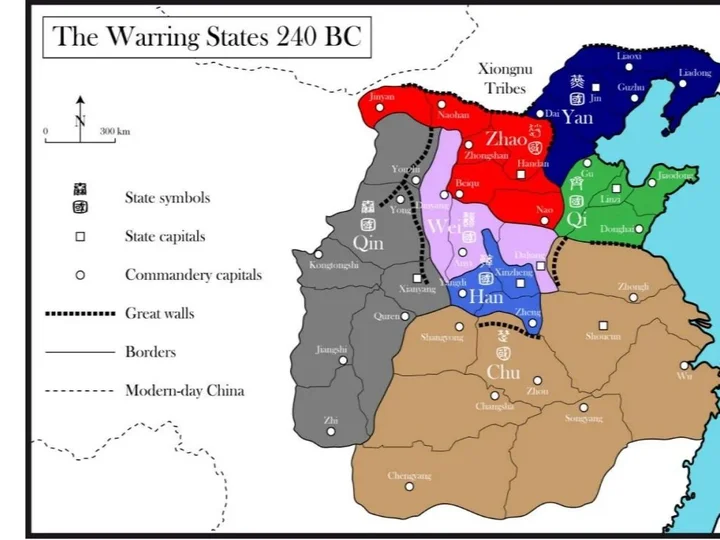
3-3. Zhou Dynasty (1046 BC- 256 BC, 791 years)
Spring and Autumn Period (770 BC- 476 BC, 294 years)
The Spring and Autumn Period was the period when the first nationwide division was formed in Chinese history. Historians generally regard "Three Schools Dividing Jin" as the end of the Spring and Autumn Period and the beginning of the Warring States Period. In 770 BC, the Eastern Zhou Dynasty had weakened to the extreme, and its ruling area was less than 600 li. The various vassal states had cut off their feudal lords and no longer met the Zhou King, and their right to lead the vassals existed in name only. During this period, the country was divided into more than 140 large and small vassal states, of which Chu, Qi, Jin, Wu, Yue, and Qin were the largest.
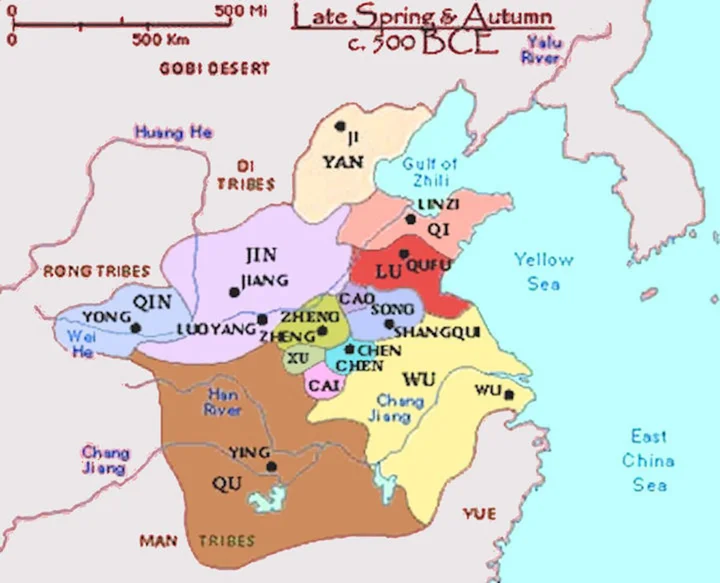
3-4. Zhou Dynasty (1046 BC- 256 BC, 791 years)
Warring States Period (475 BC- 221 BC, 264 years)
The Warring States Period was a period of great change in Chinese history following the Spring and Autumn Period. The Warring States Period includes before the demise of the Zhou Dynasty, and after the Zhou Dynasty, before the Qin annihilation of the six kingdoms was completed. The Eastern Zhou Dynasty was destroyed by the Qin State in 256 BC. After the protracted war for hegemony during the Spring and Autumn Period, the number of vassal states in the Zhou Dynasty was greatly reduced. The result is the symbol and established the pattern of the Seven Heroes of the Warring States Period. After the three kingdoms were divided into Jin, Zhao, Wei, and Han were among the powerful countries, and the Tian clan replaced Qi, and the pattern of the seven heroes of the Warring States was officially formed. The seven kingdoms were: Qi, Chu, Yan, Han, Zhao, Wei and Qin State.
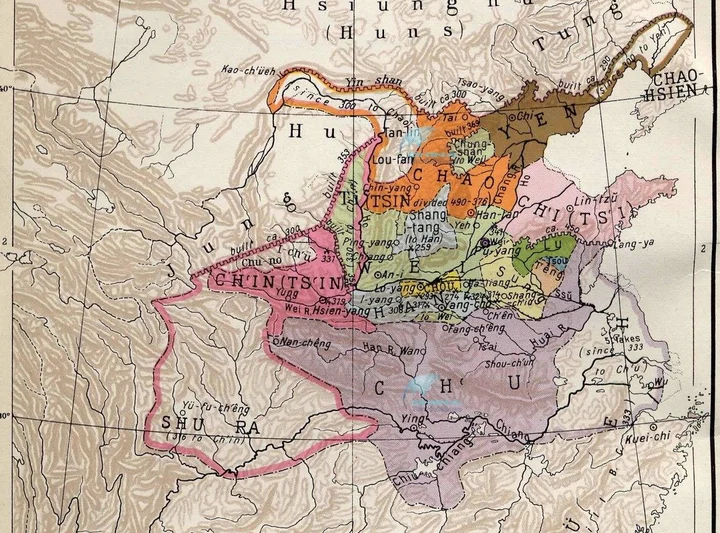
4. Qin Dynasty (221 BC- 207 BC, 15 years)
The king of Qin, Yingzheng destroyed six kingdoms, established the first unified feudal dynasty in Chinese history, and ended the split of the Spring and Autumn and Warring States for hundreds of years. The Qin Dynasty Guozuo did not last long. It was passed down for three generations, with two emperors and one king. The Guozuo lasted for fifteen years. In 207 BC, Qin Ziying surrendered to Liu Bang and the Qin Dynasty perished. The royal family of the Qin Dynasty had the surname Ying, so it was also called Ying Qin in the history books to distinguish it from the regime of Qin in other countries. Qin Shihuang established the emperor system, the central government implemented the three princes and nine ministers, the local abolition of the feudal system, replaced the county system, unified writing and weights and measures, attacked the Xiongnu in the north, conquered Baiyue in the south, and built the Great Wall. It pushed China into the era of great unification, created a new situation for the establishment of an authoritarian centralized system, had a profound impact on the history of China and the world, and established the basic pattern of China's political system for more than 2,000 years. He was hailed as "one emperor through the ages" by the Ming Dynasty thinker Li Zhi.
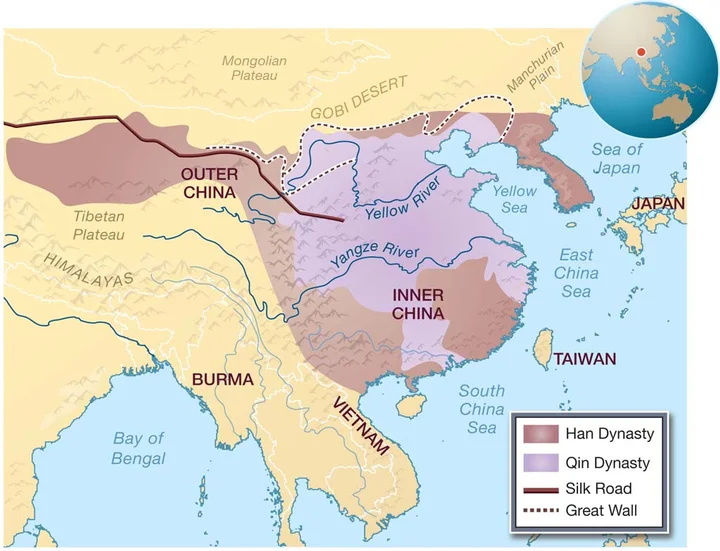
5. Western Chu Dynasty (206 BC- 202 BC, 5 years)
The Western Chu Dynasty was a regime that emerged after the Qin Dynasty in Chinese history. It was also a dynasty between the Qin Dynasty and the Han Dynasty. It was built by Xiang Yu. In April 206 BC, most of the territory of the Qin Dynasty was nominally unified. The capital was established in Pengcheng (now Xuzhou, Jiangsu). At the end of the Qin Dynasty, a peasant uprising broke out. For a time, the Quartet responded, and the world was in chaos. Xiang Liang and Xiang Yu, the nobles of the former Chu State, took advantage of the situation to rise. Xiang Yu enfeoffed eighteen princes in Xianyang, and established himself as the overlord of Western Chu. In 202 BC, Liu Bang joined Han Xin, Peng Yue, and Yingbu with 500,000 troops to encircle Xiang Yu at Gaixia. Xiang Yu was defeated and killed himself in the Wujiang River. Lu Matong, Yang Wu, Lu Sheng, Yang Xi, and Wang Yi divided his body.
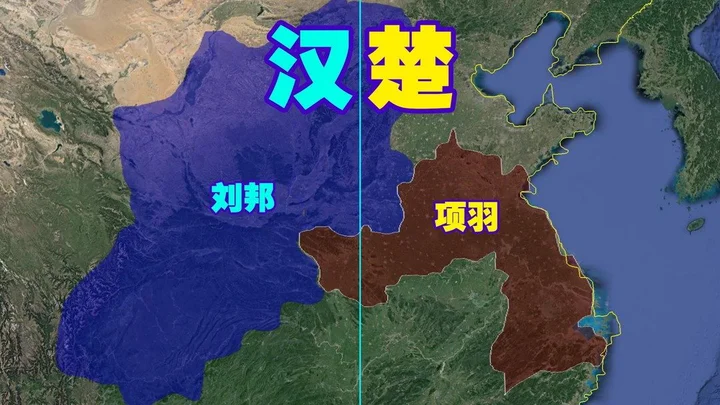
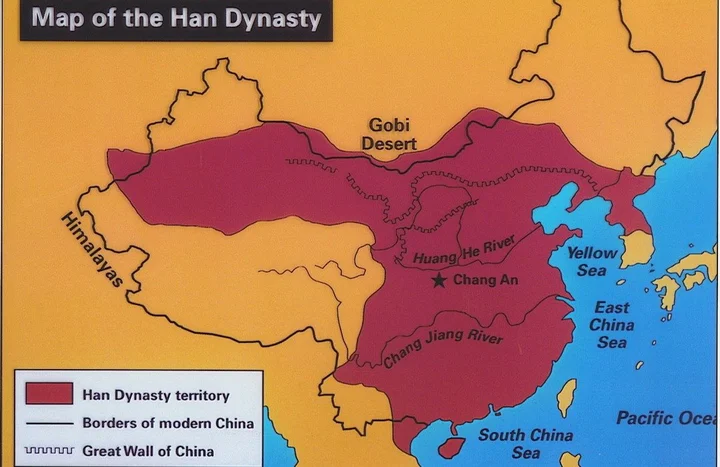
6. Western Han Dynasty (202 BC- 8 AD, 210 years)
In 202 BC, Liu Bang founded the country and made Chang'an the capital. After the reign of Wenjing, Emperor Wu of the Han Dynasty, Liu Che, further promoted the unified affairs, and reached its peak during the "Zhaoxuan Zhongxing". The Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire in Europe around the same period were listed as the most advanced civilization and powerful empire in the world at that time. During the two Han Dynasties, the scope of Han land was established. At its peak, it bordered North Korea in the east, Vietnam in the south, Congling in the west, and Gobi in the north, with a land area of about 6.09 million square kilometers. In 2 AD, the population of the Western Han Dynasty reached more than 60 million, accounting for one-third of the world at that time. The Han Dynasty was the first golden period in the history of China's development. The Han nationality got its name during this period. Due to its high degree of civilization, the Han nationality has always been in a dominant position among the fraternal ethnic groups in China. This is the result of historical development and natural formation.
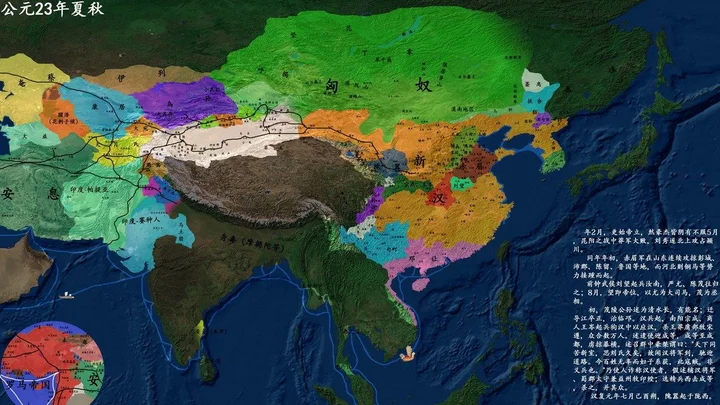
7. Xin Dynasty (8 AD - 23 AD, 16 years)
The New Dynasty was established by Wang Mang, a foreign relative of the Western Han Dynasty after the Western Han Dynasty. In the twelfth lunar month of AD 8, Wang Mang abolished Han Ruzi (Liu Ying) as Duke Anding, changed the country name to Xin, and established the capital Chang'an (now the ruins of Han Chang'an City in Xi'an), known as Xinmang in history. Wang Mang's reformation failed, the history of existence was too short, and there was no successor, and he was considered a usurper.